Blockchain & AI Use Cases
Blockchain technology has a wide array of potential applications beyond cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin. Here are a few examples:
Where Blockchain can be used:
- Supply Chain Management: Blockchain can provide a transparent and unchangeable record of the entire history of products — from manufacture to sale. This can help with authenticity, prevent fraud, and ensure compliance with regulations.
- Healthcare: Patient records can be encoded and stored on the blockchain with a private key, so that they are only accessible to specific individuals, thereby ensuring privacy and security.
- Financial Services: Beyond cryptocurrencies, blockchain can revolutionise payments, increase the speed of transactions while reducing their cost, and improve the security of transactions.
- Real Estate: Recording property ownership could be vastly improved using blockchain technology. It would make it easier to verify legal documents, transfer ownership, and check the history of a property.
- Voting Systems: Blockchain could be used to create tamper-proof and transparent voting systems, potentially reducing fraud and making the electoral process more credible.
- Intellectual Property and Royalties: For artists and creators, blockchain can provide a secure and unchangeable ledger of intellectual property rights and ensure that they are compensated for usage.
- Identity Verification: Blockchain could serve as a means to prevent identity theft and fraud, with individuals controlling their digital identity and personal data.
- Internet of Things (IoT): Blockchain can secure the vast number of devices connected to the internet by maintaining a secure and unchangeable record of transactions.
- Legal Industry: Smart contracts can automate and enforce contractual agreements in the legal industry, with the blockchain providing a secure and unchangeable record of the agreement and its execution.
- Education: Blockchain can be used to permanently secure and validate educational credentials, simplifying the verification process for employers and institutions.
- Food Safety: By tracking the production, shipment, and delivery of products in a blockchain, consumers can trace the source of food items and businesses can better manage recalls.
- Energy Trading: Blockchain enables more efficient and transparent energy trading, particularly with the rise of microgrids and localised energy generation.
These examples illustrate the breadth of blockchain’s potential impact. As blockchain technology evolves and matures, it’s likely that new and innovative uses will continue to emerge across various industries.
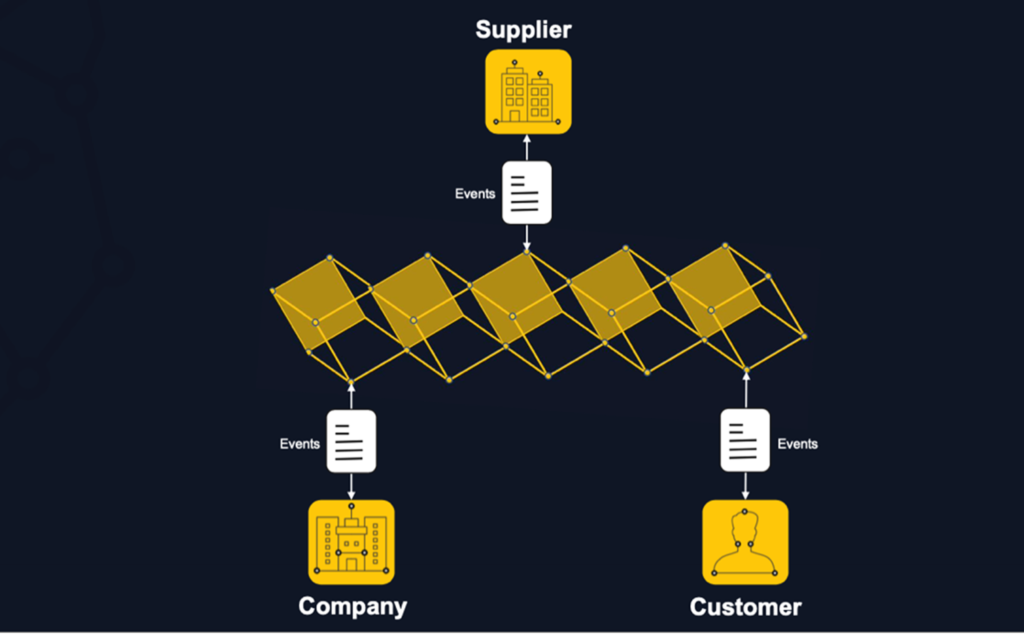
Supply Chain
A blockchain implementation across the whole supply chain process will allow every user (with sufficient rights), from producer to consumer, to use, share, edit and connect the same information regarding a product or a service, and make sure the data and product are authentic.
For Reusable Transport Items (RTI) this means greater logistical efficiency, transparency between parties, streamlined administration, and less balance reconciliation, resulting in a more sustainable supply chain with fewer lost items.
Building and Construction
Blockchain solutions in the Construction and Building business are bringing big benefits.
1.Supplier Identity Management:
- Onboarding Suppliers: Suppliers are onboarded onto the blockchain platform, with each supplier given a unique digital identity.
- Verification: Verification process for suppliers’ credentials and past work history, ensuring trust and reliability.
2. Project Management on Blockchain:
- Smart Contracts: Smart contracts can be used for automating and enforcing agreements with suppliers.
- Task Assignment and Tracking: Tasks are assigned to suppliers on the blockchain, with real-time tracking of progress and automated updates.
- Quality Control and Compliance: Blockchain is used for maintaining quality control and ensuring compliance with regulations and standards.
3. Feedback Mechanism:
- Feedback from Suppliers: Suppliers can provide feedback and updates on their progress using the blockchain platform.
- Feedback to Landlord: You can efficiently compile and present progress reports to the landlord using data from the blockchain.
4. Payment and Incentives:
- Automated Payments: Payments are automated and released upon task completion, as verified on the blockchain.
- Incentives for Timely and Quality Work: Incentive mechanisms for suppliers to encourage timely and quality work.
5. Security and Data Integrity:
- Encryption and Data Protection: Security features of the blockchain, like encryption, to protect sensitive project data.
- Immutable Records: The blockchain ensures that records cannot be altered, ensuring data integrity.
The Implementation of Blockchain-based document passports offers a secure and immutable solution to manage critical construction documents, such as permits, contracts, and blueprints. This results in reducing the administrative burden by 50-80%.
Contact
Office: +44 (0)1256 592997
info@nexusdigitalconsulting.co.uk